UDA Training: Glucagon Administration
Diabetes Aide TrainingComplete all of the following modules:
As you complete this training course the RN responsible for delegating the task of insulin administration should be available to discuss the content and answer your questions.
Glucagon Administration
What is glucagon?
Glucagon, like insulin, is a hormone that the body produces in the pancreas. As you recall, insulin moves glucose (sugar) out
of the blood and into cells. Glucagon does the opposite!
When a person has a low blood sugar the pancreas releases the glucagon into the bloodstream. The glucagon causes the liver to
release stored glucose (sugar). This glucose then enters the blood stream to help raise the body’s blood glucose level back to
normal.
When should glucagon be given?
Glucagon should be given when a person has severe hypoglycemia. A person with severe hypoglycemia may:
- Be having seizures
- Have loss of consciousness
- Not be able to swallow (and is unable to eat food or drink liquids)
When you see any of these you need to be prepared to give the person a glucagon injection. Never try to force glucose gel,
juice, milk, or any other food or liquid into the mouth of a person who is unable to swallow safely or who is unconscious.
Where is glucagon injected?
Discuss with the RN which muscle(s) would be best for your student or patient.
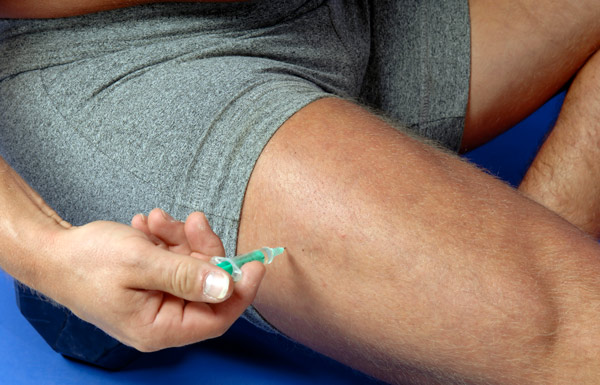
Glucagon is injected into a muscle. The large muscles of the leg or of the arm are often used because they are the easiest
muscles to get to in a hurry for most people having a hypoglycemic reaction.
How to give glucagon
Glucagon usually comes in a kit. The kit includes a syringe that is full of saline and a bottle with the glucagon powder.
You will need to mix the two together. Once the glucagon has been mixed it is only good or usable for 48 hours.
Remember to check the expiration date on the label of the glucagon kit! Discuss with the RN how to request a new glucagon kit.
Review the steps in the table to identify how to give a glucagon injection. Then watch the video. The video demonstrates the
steps and will help you prepare to practice and to safely perform this task with your delegating RN.
How to administer glucagon
Follow these steps to safely inject glucagon:
When you notice the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, initiate emergency steps:
- Activate EMS (call 911)
- Check for breathing and maintain open airway
- Check blood sugar if you have a meter
Wash hands if possible
Gather supplies Glucagon kit, gloves, alcohol and cotton balls
Verify expiration date on glucagon kit
Put on gloves
Flip the cap off the vial of powder
Remove the cap from the syringe
Inject the entire fluid from the syringe into the vial that holds the powder
Roll the vial until all the powder is dissolved The solution should be clear and colorless
Hold the vial upside down and withdraw all of the liquid solution
Check for and remove air bubbles If you see bubbles, tap syringe to raise bubbles to top, then push bubbles back into bottle.
Pull plunger back down to withdraw all solution
Withdraw needle from vial, hold syringe upright
Push plunger to correct glucagon dose Discuss the appropriate dose with your delegating RN.
Expose injection site (muscle area) and clean skin Use upper thigh or deltoid muscle in arm. In an emergency the injection can be administered through clothing.
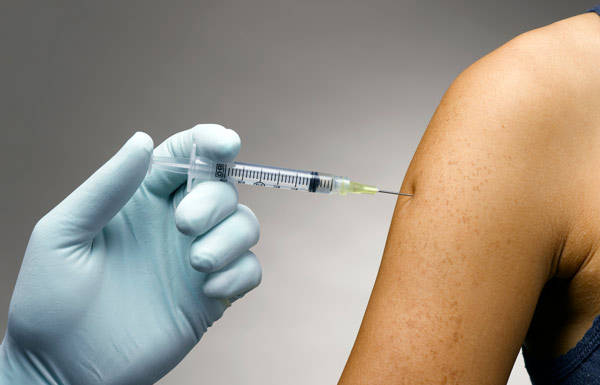
Insert needle into the skin at a 90 degree angle; then inject glucagon For smaller people, you may want to give the injection at an angle to avoid going too deep. Discuss with your delegating
RN and practice using the technique that is right for the student or patient.
Withdraw needle and hold cotton ball on site
Turn the person onto abdomen or side
Stay with the person and keep him on his side. It may take 15-20 minutes for the person to regain consciousness
Dispose of syringe and vial into sharps container
Once the person awakens, feed him some protein and carbohydrate
Document: date/time, blood glucose result if checked, amount of glucagon given, and injection site
Notify delegating RN And other family as directed
What is glucagon?
Glucagon, like insulin, is a hormone that the body produces in the pancreas. As you recall, insulin moves glucose (sugar) out
of the blood and into cells. Glucagon does the opposite!
When a person has a low blood sugar the pancreas releases the glucagon into the bloodstream. The glucagon causes the liver to
release stored glucose (sugar). This glucose then enters the blood stream to help raise the body’s blood glucose level back to
normal.
When should glucagon be given?
Glucagon should be given when a person has severe hypoglycemia. A person with severe hypoglycemia may:
- Be having seizures
- Have loss of consciousness
- Not be able to swallow (and is unable to eat food or drink liquids)
When you see any of these you need to be prepared to give the person a glucagon injection. Never try to force glucose gel, juice, milk, or any other food or liquid into the mouth of a person who is unable to swallow safely or who is unconscious.
Where is glucagon injected?
Glucagon is injected into a muscle. The large muscles of the leg or of the arm are often used because they are the easiest muscles to get to in a hurry for most people having a hypoglycemic reaction.
How to give glucagon
Glucagon usually comes in a kit. The kit includes a syringe that is full of saline and a bottle with the glucagon powder. You will need to mix the two together. Once the glucagon has been mixed it is only good or usable for 48 hours.
Review the steps in the table to identify how to give a glucagon injection. Then watch the video. The video demonstrates the steps and will help you prepare to practice and to safely perform this task with your delegating RN.
How to administer glucagon
Follow these steps to safely inject glucagon:
|
|
| Glucagon kit, gloves, alcohol and cotton balls | |
| The solution should be clear and colorless | |
| If you see bubbles, tap syringe to raise bubbles to top, then push bubbles back into bottle. Pull plunger back down to withdraw all solution | |
| Discuss the appropriate dose with your delegating RN. | |
| Use upper thigh or deltoid muscle in arm. In an emergency the injection can be administered through clothing. | |
| For smaller people, you may want to give the injection at an angle to avoid going too deep. Discuss with your delegating RN and practice using the technique that is right for the student or patient. | |
| It may take 15-20 minutes for the person to regain consciousness | |
| And other family as directed |